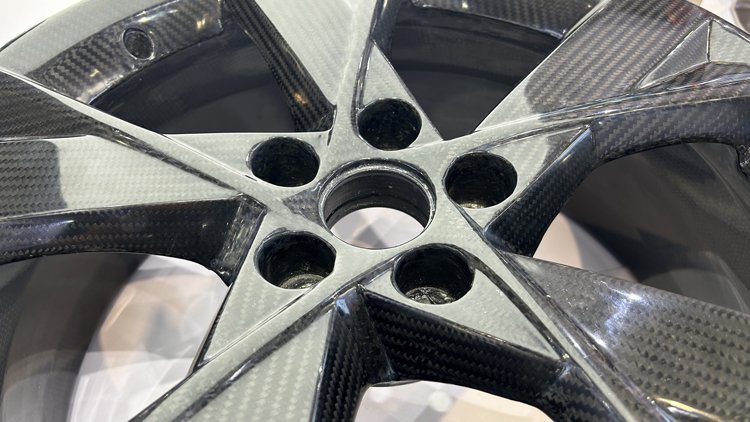
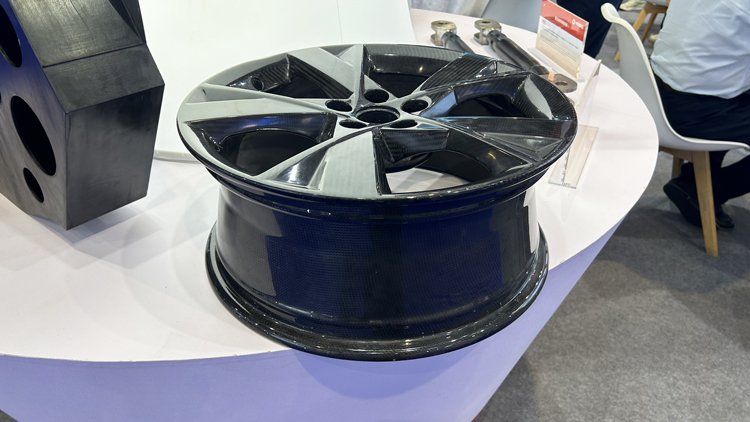
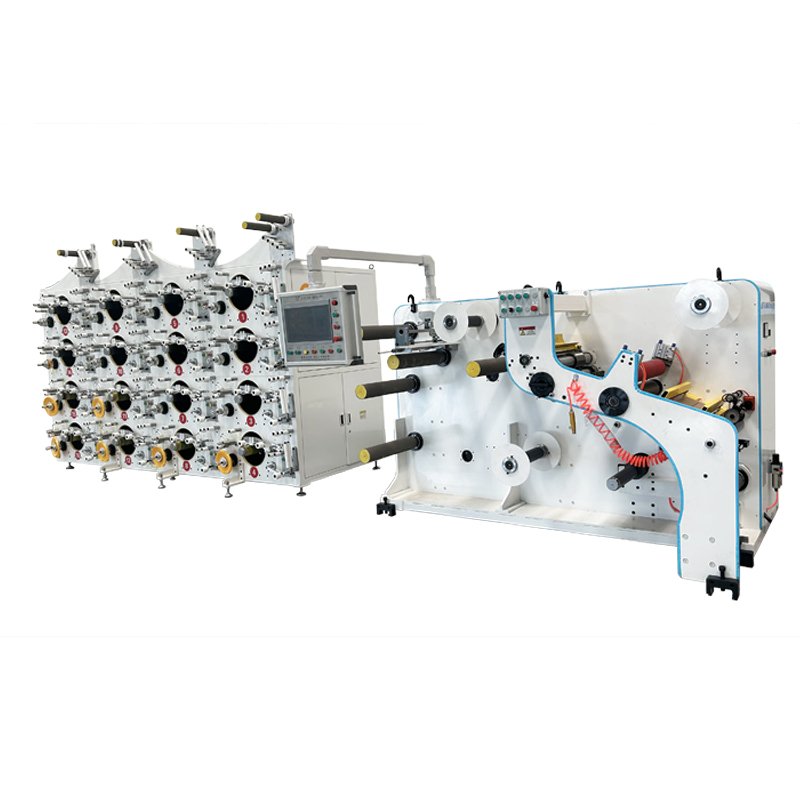
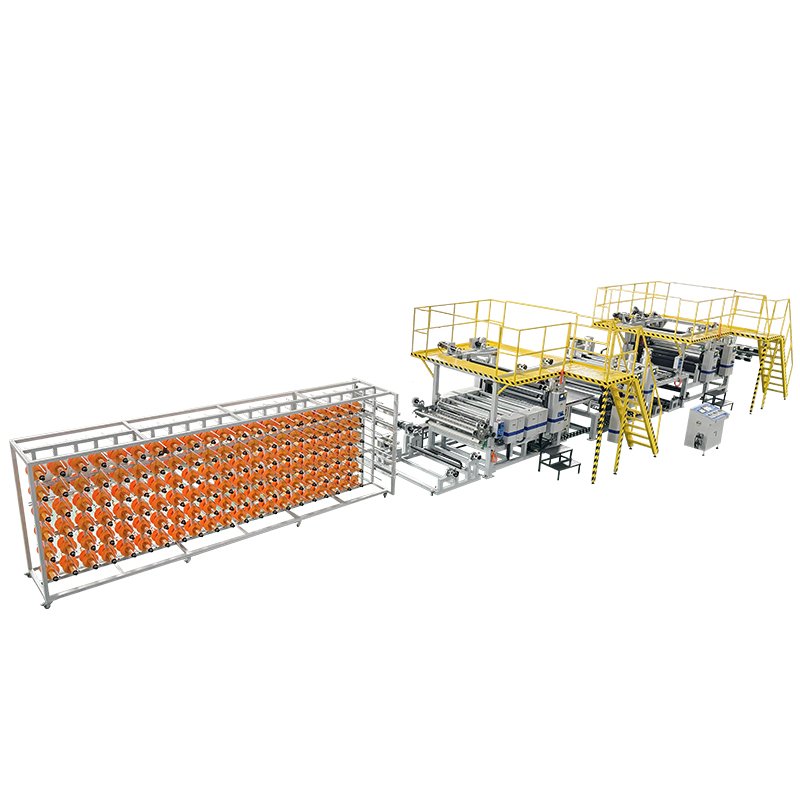
Continuous Fiber Reinforced Composites Service
- Advanced hot melt impregnation method
- Carbon fiber,basalt fiber,aramid fiber,glass fiber
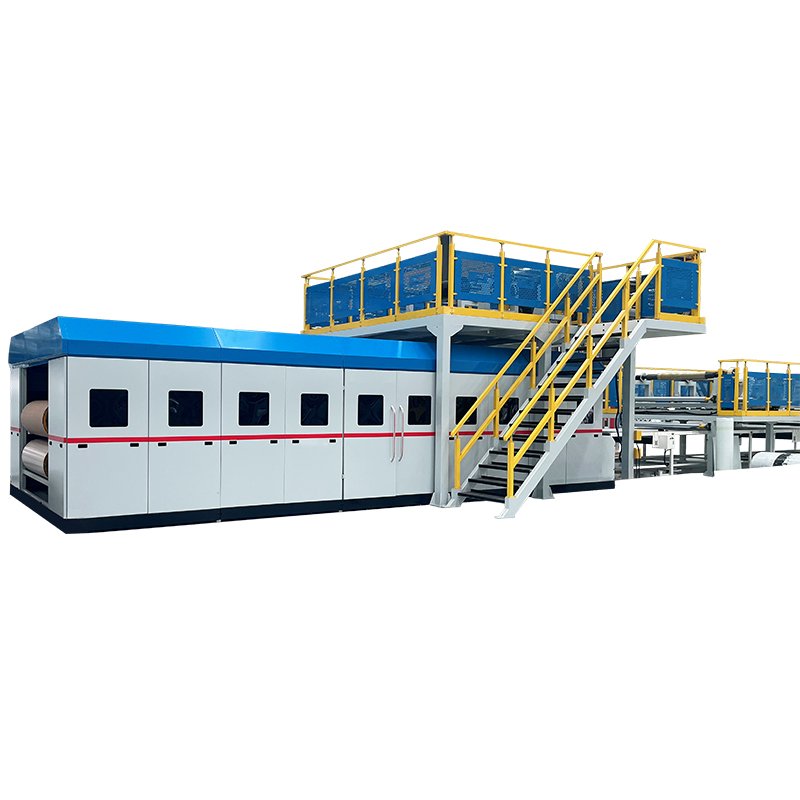
- From prepreg machine to double belt press machine
- Filed:aerospace, electric vehicles, refrigerated containers, wind power
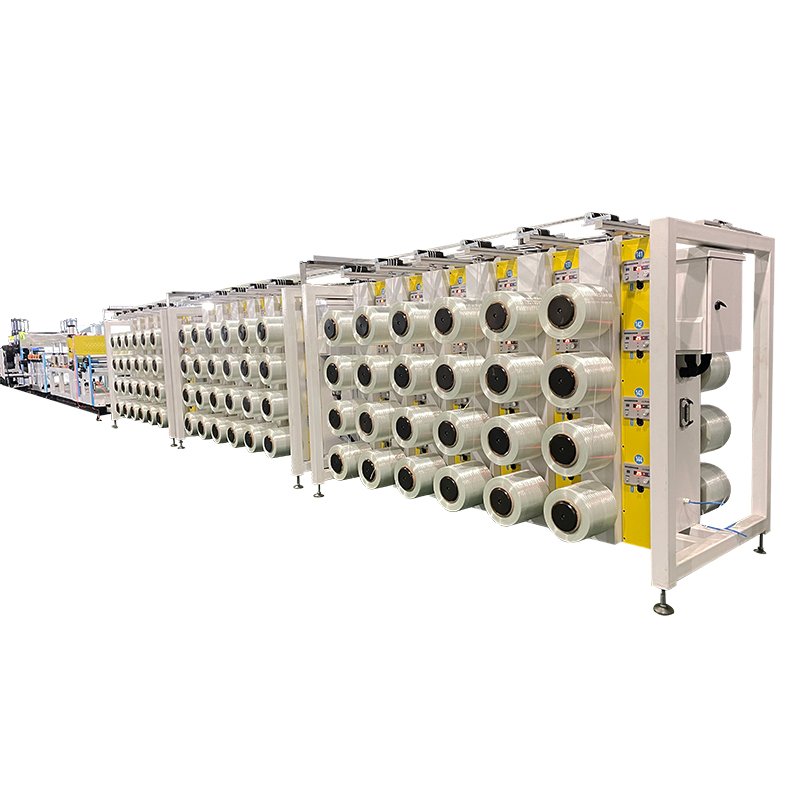
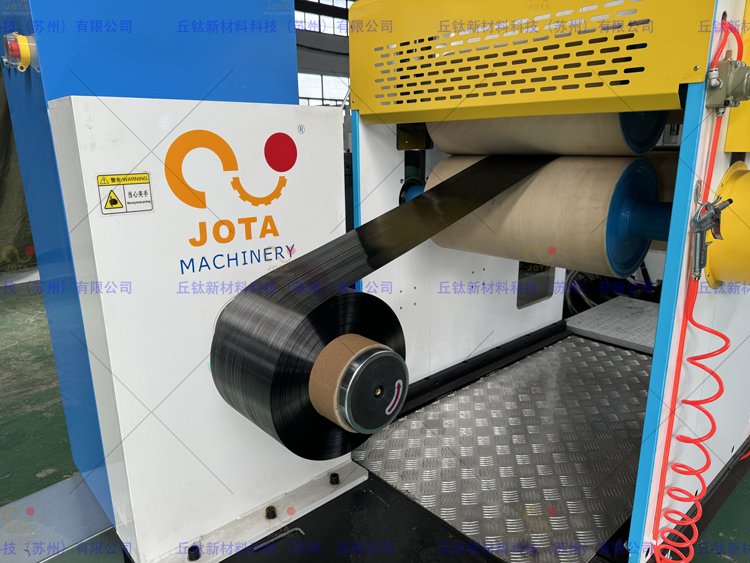
Jota CFRP CFRTP Hot Melt Prepreg Machine
Our Jota CFRP CFRTP prepreg manufacturing machines are ideal machines for CFRP CFRTP prepreg production.
CFRP and CFRTP prepregs are essential raw materials for the production of high-performance carbon fiber and glass fiber composite materials.
If you are looking for prepreg machines, please send us an inquiry on this website.
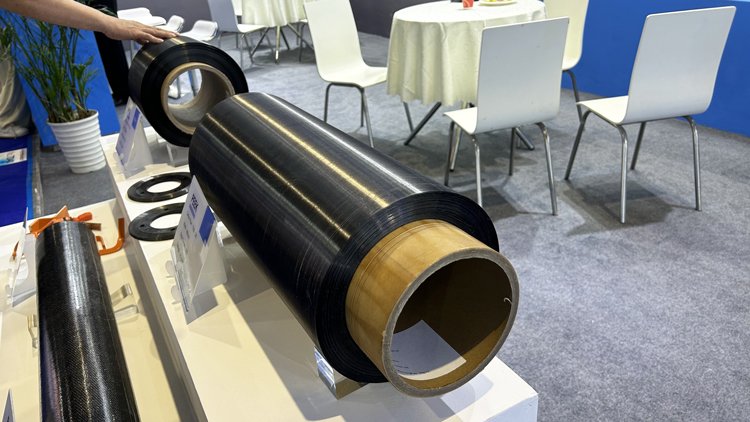
CFRP CFRTP Prepreg Conversation
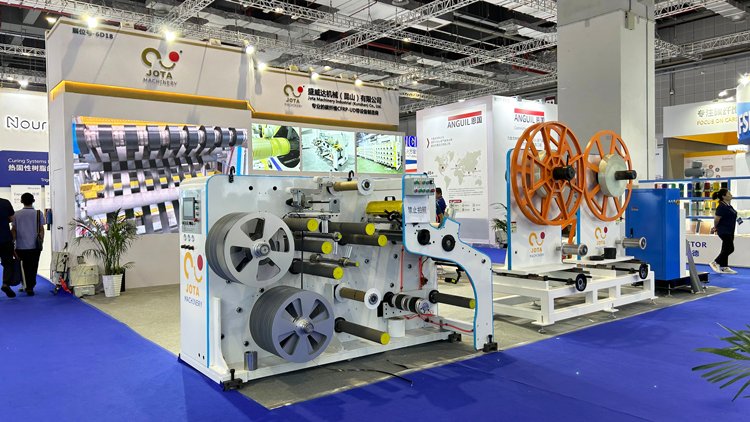
Jota Machinery: Your Reliable CFRTP CFRP Prepreg Machine Manufacturer in China
Jota is the original CFRTP CFRP prepreg machine manufacturer here in China.
With our own factory and CNC center, equipment quality could be effectively guaranteed.
Please send us an inquiry to make a WhatsApp video call, let’s show you our real-time factory and CNC center.
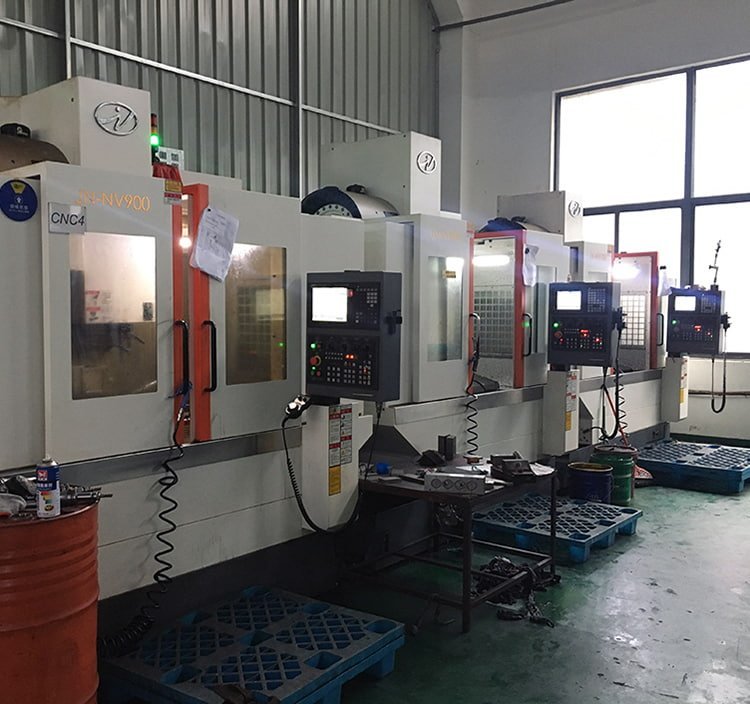

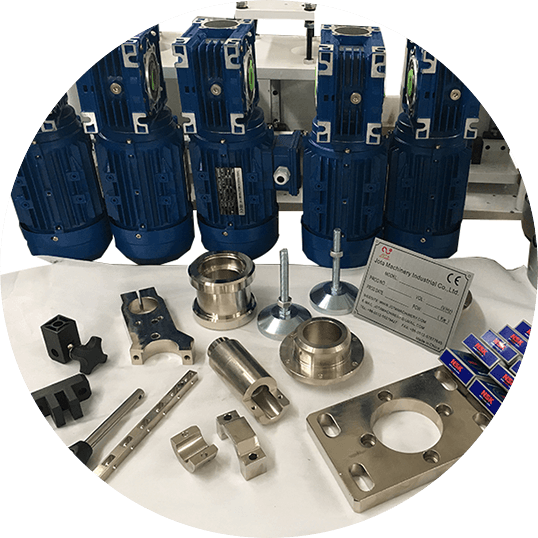
Jota CNC Center
Machining Material
- Visible high-quality components.
- Famous brands such as Siemens, Yaskawa, Delta, Schneider, Mitsubishi.
- Self-supporting CNC processed sheet metal, precision parts.
- Assembly raw materials provided by long-term cooperation suppliers.


Installation and operation user manual, wire connection diagram, tension controller guide.
Installation and operation video tutorial.
One-on-one remote video call assistance.
On-site installation and operation guidance.
- Focus Factory
- Dear Customer
- Professional Team
Around 30-45 days, mainly depends on machine type.
Sure, it is our honor to work for you.
We will offer you some parts as backup, in case any part is broken within one year, we will sent you for free.
Sure, if we have client in your country, we will offer.
Advancements and Applications of Composite Materials: A Comprehensive Exploration Across Industries
When it comes to composite materials, people often associate them with the black carbon fiber commonly found on high-end sports cars. However, the applications of composite materials extend far beyond this.
In essence, composite materials are formed by combining two or more different materials.
One of the materials serves as the matrix, while the others act as reinforcing phases.
The matrix is typically continuous, and the reinforcing phase can be in the form of particles, fibers, or laminates.

With the functional development of polymer plastics, the earliest polymer-based composite material, glass fiber-reinforced unsaturated polyester resin, known as fiberglass-reinforced plastic, emerged in the United States in 1942.
As industrial advancements occurred, fiber-reinforced polymer composites with high stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios gained increased attention.
Dating back to ancient Mesopotamia, composite materials were already used as construction materials when plywood was invented.
One of the most common modern construction materials is composite materials, incorporating different substances such as wood as a reinforcement and glue as the matrix.
Other historically significant composite materials include huts made from grass (reinforcement), mud (matrix), and paper.
Composite materials consist mainly of two components: the matrix and the reinforcing phase.
The matrix plays a crucial role in bonding the reinforcing phase into a cohesive whole, transferring loads to the reinforcing phase and bearing the load and stress.
Typically, high-polymer materials with high chemical stability, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability, such as resins, rubber, and polyimides, are chosen as matrices.
The matrix also provides protection to the reinforcing phase.
The reinforcing phase is the component in composite materials that bears the load, enhancing the strength and stiffness of the composite material.
Major reinforcing phases include fibrous materials like inorganic glass fibers, carbon fibers, basalt fibers, and some ceramic fibers like silicon carbide.
Organic fibers such as aramid fibers are also used. The synergistic cooperation between the matrix and the reinforcing phase creates new materials with superior performance.
Various materials in composite materials complement each other in terms of performance, producing synergistic effects that result in comprehensive performance superior to that of the original materials.
Composite materials offer many advantages over traditional materials, including high strength-to-weight ratio, high fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, enhanced friction and wear resistance, low thermal conductivity, low coefficient of thermal expansion, and adjustable material properties to meet design requirements.

For example, ceramic materials exhibit high-temperature resistance but are relatively brittle.
To enhance toughness, high-strength, high-elasticity fibers can be combined with ceramic matrices, creating composites used in liquid rocket engine nozzles, missile antenna covers, aerospace aircraft nose cones, aircraft brake discs, and high-end automobile brake discs, forming a crucial branch of high-tech new materials.
Based on the type of reinforcing phase, composite materials can be categorized as follows:
- Particulate Composites
- Continuous or Short-Fiber Composites
- Continuous Fiber Composites
According to the type of matrix material, composite materials can be classified as:
- Polymer Matrix Composites
- Metal Matrix Composites
- Ceramic Matrix Composites
- Carbon Matrix Composites
Due to their excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and impact resistance, composite materials find wide applications in aerospace, construction, corrosion protection, pipelines, water treatment, and other fields.
Over time, the application of composite materials has expanded from military and chemical industries to various sectors of social production, with composite materials being ubiquitous in various industries.
In the aerospace sector, composite materials are extensively used due to the high requirements for material quality and strength.
For instance, on both fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft, a large number of load-bearing and non-load-bearing composite components, such as carbon fiber and glass fiber-reinforced composites, are widely employed.
These materials are used in various parts such as cabin doors, wing beams, air brakes, horizontal tail structures, fuel tanks, auxiliary fuel tanks, cabin wall panels, floors, helicopter rotor blades, propellers, high-pressure gas containers, antenna covers, nose cones, landing gear doors, fairings, and engine compartments.
In modern light aircraft, lightweight composite materials are heavily utilized.
Carbon-carbon composites can be used in high-temperature environments, such as aircraft brake discs and liquid rocket engine casings.
Additionally, composite materials are extensively used in the repair of damage to metal structures in aircraft.
The automotive industry is one of the active fields for the application of composite materials, with uses in over a hundred components such as car bodies, drive shafts, bumpers, chassis, springs, and engines.
For example, the drive shaft of small cars manufactured by Ford Motor Company uses a hybrid composite of carbon fiber and glass fiber, weighing only 5.3 kg, which is 4.3 kg lighter than steel components.
In heavy-duty trucks, the weight of the composite drive shaft is 37 kg, 16 kg lighter than steel components.
These composite components possess characteristics such as high rigidity, high natural frequency, lightweight, and good vibration damping, making them suitable for high-speed driving.
The use of composite materials for car springs can enhance impact toughness and reduce costs.
The use of hybrid composite materials for car body shells can reduce vehicle weight, increase speed, save fuel, and the use of composite materials in car engines can reduce vibration and noise, improve lifespan and speed, and enhance transport capabilities.
In shipbuilding, fiberglass-reinforced ships are widely used, with a total number exceeding 500,000.
Deep-sea submarines made of fiberglass can dive to a depth of 4,500 meters, while fast yachts use carbon fiber composite materials and CF/GF hybrid sandwich structures.

These composite materials allow ships to undergo significant deformation upon impact to absorb energy and then recover.
In the medical field, the application of composite materials is gradually expanding, such as prosthetics made of fiber-reinforced resin composites, and artificial bones and joints made of hybrid composites.
By adjusting the hybrid ratio and method, these materials can match the thermal expansion of artificial bones within the human body temperature range, thus alleviating patient discomfort.
Jota Machinery is a distinguished machinery manufacturer specializes in the production of machinery for paper converting and continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic and thermoset composite materials.

Our commitment to excellence has propelled us to serve diverse industries with a strong focus on aerospace aviation, wind turbine manufacturing, automotive engineering, and the production of reinforced thermoplastic pipes.
As of 2023, we take pride in our extensive experience and contributions to these 4 key fields, establishing ourselves as a trusted partner in the manufacturing sector.
Our dedication to quality and innovation sets us apart, ensuring that we deliver cutting-edge solutions to meet the evolving demands of these industries.
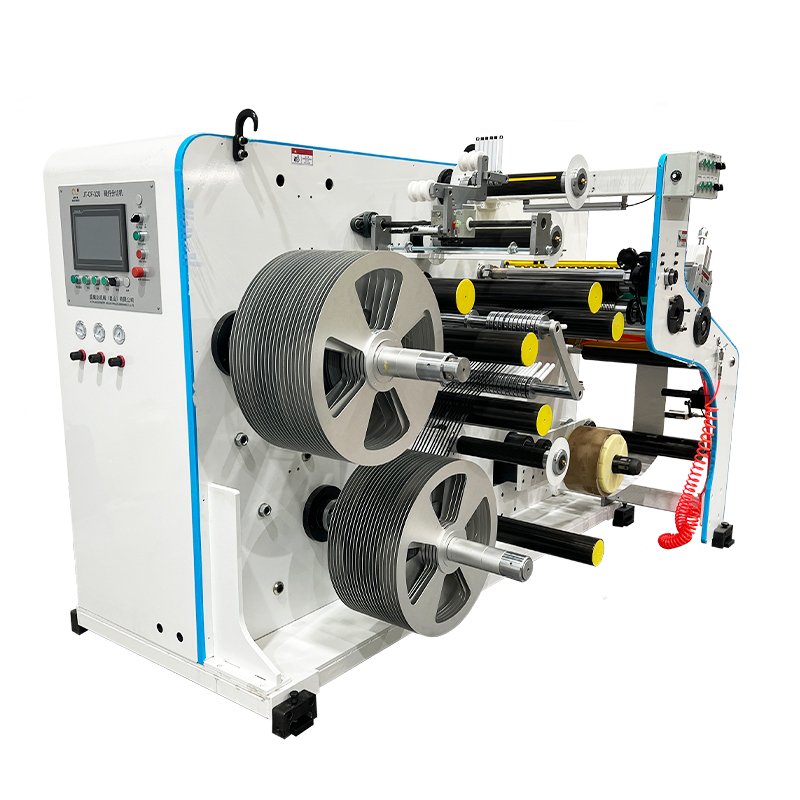
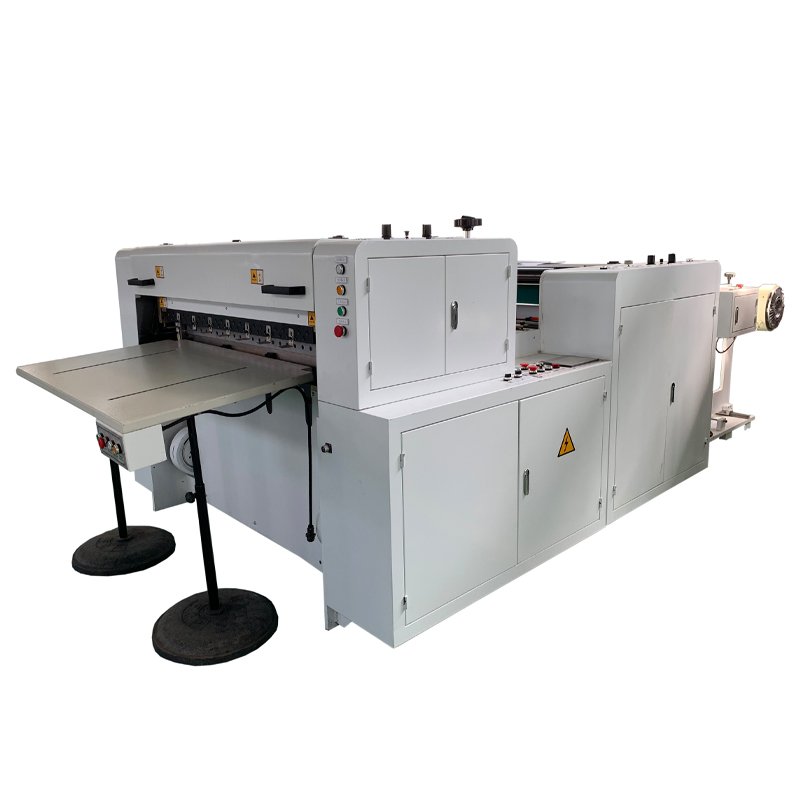
Whether you are in search of a prepreg machine, a uni-directional (UD) prepreg slitting machine, or a double belt press machine, Jota Machinery provides a comprehensive one-stop solution for all your machinery needs.
Our diverse range of machinery is designed to cater to the specific requirements of each industry we serve.
For further information or to discuss your unique requirements, we encourage you to reach out to us.
At Jota Machinery, we are committed to providing not only machinery but also expertise and support to help you thrive in the dynamic landscape of manufacturing.
Your success is our priority, and we look forward to being your trusted partner in advancing your manufacturing capabilities.