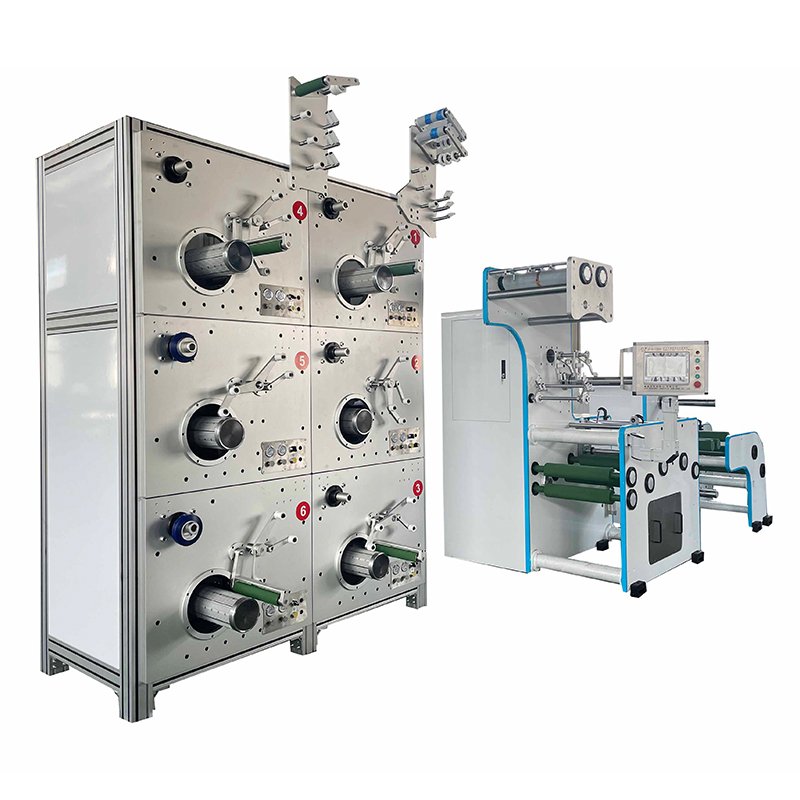
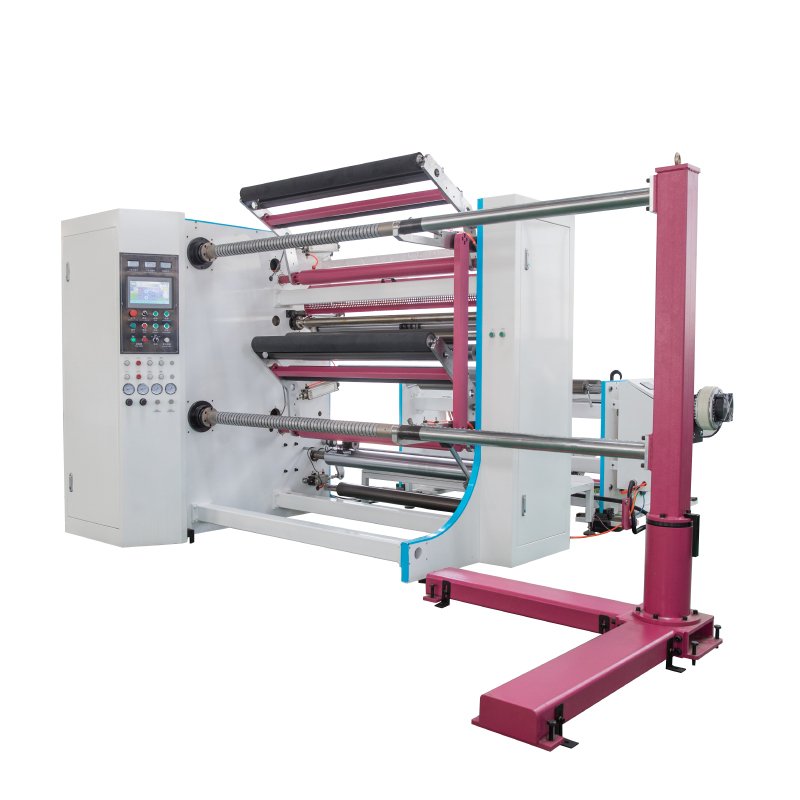
Aerospace Technology Technical Team
- High-end technology used in aerospace
- Leading AFP Technology Manufacturer
- Profession service team
- First-class advanced equipment
Automated Fiber Placement Technology
In 2021, our composite products will extend from the original continuous thermoplastic fiber-reinforced ud tape line, unidirectional tape slitting traverse spooling machine to the automated fiber placement technology used in aerospace.
We provide not only equipment but also a mutually beneficial overall solution. Please contact us if you need any assistance.

Leading Automated Fiber Placement Manufacturer
Jota is able to manufacture 3 sets of automated fiber placement equipment in 3 month with our own CNC center.
Foothold wall and precision parts could be made by ourselves, machine quality could be guaranteed.
You could just send some prepreg materials to us, we could test it, then share the testing video with you.
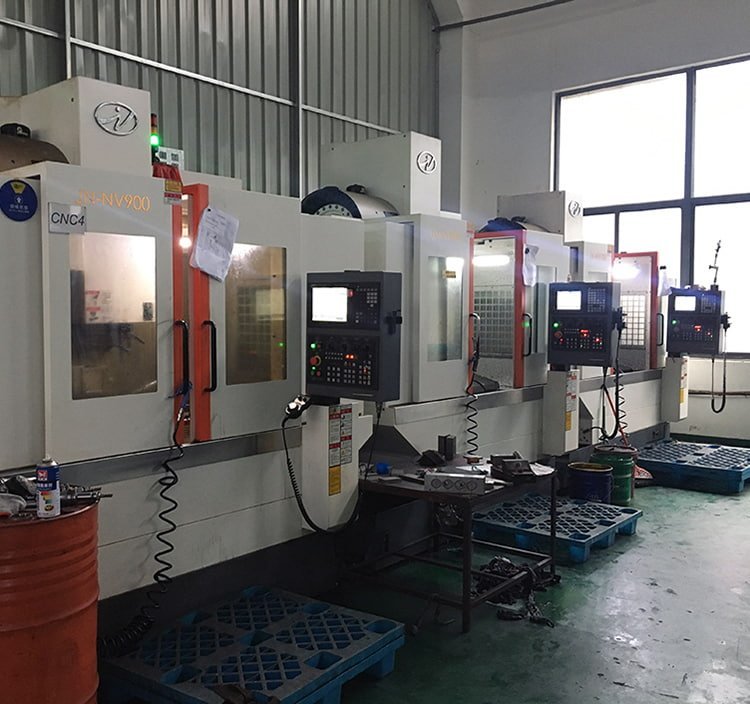

Jota CNC Center
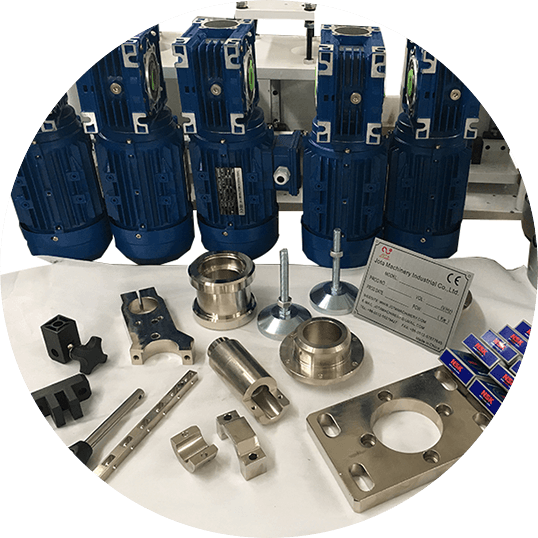
Machining Material
- Visible high-quality components.
- Famous brands such as Siemens, Yaskawa, Delta, Schneider, Mitsubishi.
- Self-supporting CNC processed sheet metal, precision parts.
- Assembly raw materials provided by long-term cooperation suppliers.


Installation and operation user manual, wire connection diagram, tension controller guide.
Installation and operation video tutorial.
One-on-one remote video call assistance.
On-site installation and operation guidance.
- Focus Factory
- Dear Customer
- Professional Team
Around 30-45 days, mainly depends on machine type.
Sure, it is our honor to work for you.
We will offer you some parts as backup, in case any part is broken within one year, we will sent you for free.
Sure, if we have client in your country, we will offer.
Automated Fiber Placement Technology
Last Update Time:29/03/2022
Thanks to the advent of technology, composite structures are now dominating the energy, automotive, and aerospace markets. You may ask how as you doubt the quality of such structures.
Well, it’s through a manufacturing process known as Automated Fiber Placement (AFP). With this process, composite materials get enhanced to match the strength of metals or even beyond. Also, compared to metals, composite materials processed through AFP come lighter in weight.
At Jota Machinery, we have embraced the technology and are making Automated Fiber Placement machines to be used in various manufacturing sectors. In return, manufacturers don’t have to worry about human error or long production cycles.
You are on the right page if you are new to AFP or want to learn more about fiber placement machines from Jota Machinery. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about Automated Fiber Placement.
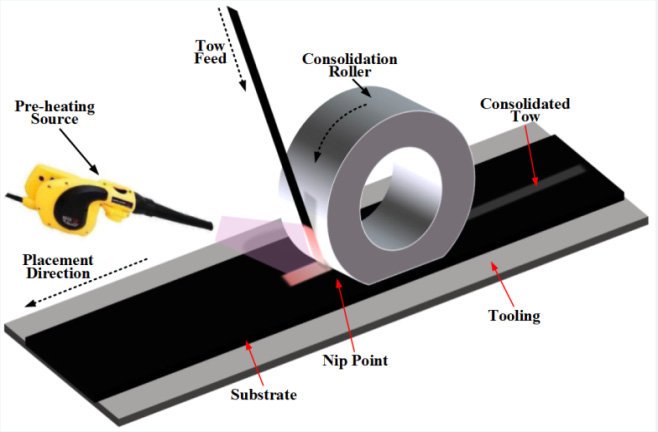
The process is complex and entails a couple of phases discussed here. But before then, let’s learn how this intriguing technology came about for a better understanding.
Evolution of Automated Fiber Placement
It all started with research by a renowned scholar named Watt et al. in 1966. According to his findings, carbon fiber materials were fit for commercial use. But on further investigation, he discovered that the manufacturing process would be extensive.
Therefore, automating the process would help out. That’s how Automated Fiber Placement started. Its discovery was with another automated process known as Automated Tape Laying (ATL).
The ATL process imitates the unidirectional (UD) tape of 75 mm to 300 mm wide manual layup. The only difference is that this procedure deals with more significant parts at a higher speed. Also, the surfaces curve slightly more than the manual process, and the ATL process has greater control.
It’s a different case with AFP. The procedure entails a robotic or gantry system consisting of a fiber placement head. Various composite materials or tow strips get laid on a tool surface through the AFP head.
Through the AFP process, you can create either;
- Course: It entails tow series
- Ply: It’s a combination of several courses
- Laminate: The formation consists of attaching many plies
Ten years later, reviews of certain scholars like Lukaszewicz indicated enormous progress in automated prepreg layup. They also discovered that the AFP field had also enjoyed tremendous advancements. This field also created many opportunities.
Due to technology advancement and better innovations, the AFP process advanced in;
- Design
- Process planning
- Manufacturing
- Inspection
Because the technology improves continually, the above AFP processes will also keep changing. This improvement cycle presents many challenges within the AFP industry, but it’s worth doing it.
For optimal results, this technology kept on improving. As a result, the AFP industry settled for a closed-loop workflow. And what could this be? Here is the answer;
Closed Loop AFP Workflow
It entails interconnecting the above AFP processes. The process creates specialization where the personnel and data from each department get isolated. The interaction is very minimal to maximize the process.
Also, unlike before, where designing was the initial process, the closed-loop workflow makes it a continuous process integrated into the other phases.
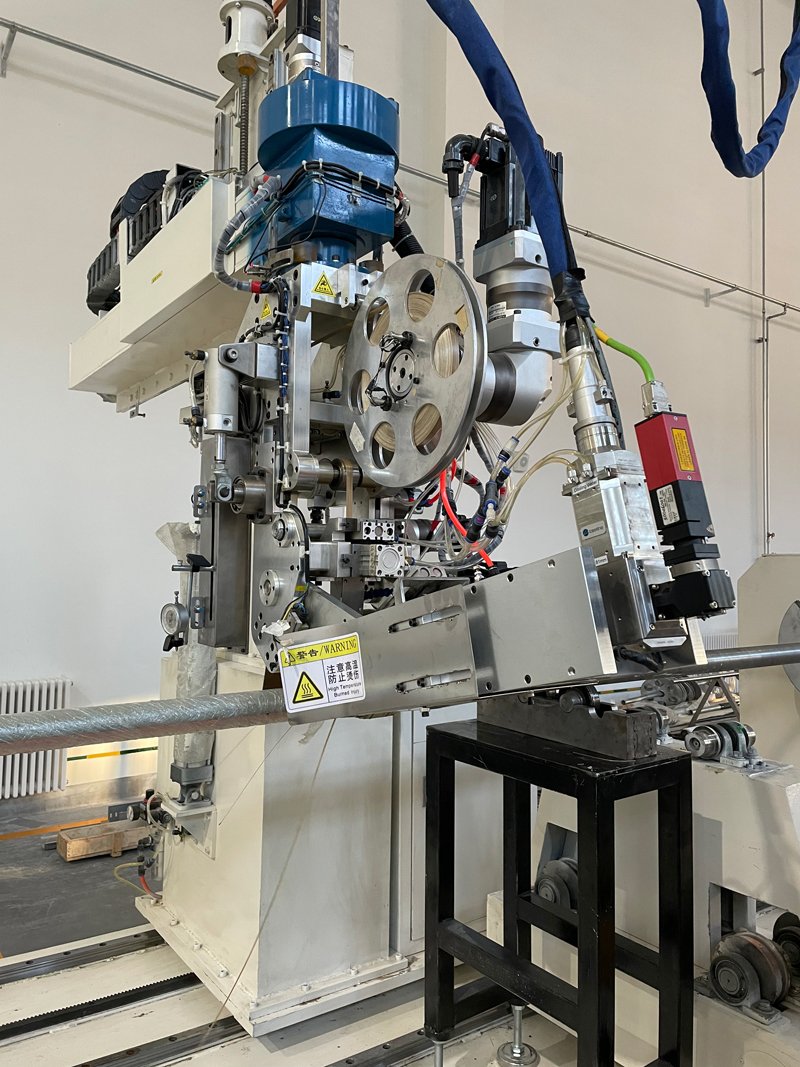

Though the closed-loop workflow process has its challenges, it’s a better option. With time, various mechanisms developed, which led to the formation of fiber placement machines. It happened as follows;
Development of Fiber Placement Machines
Before the AFP technology came along, large composite structures were made with filament winding and ATL. By that time, tapes were already being used.
But starting in 1974, they started using tows. This was because they invented a way to split the fibers, which was the basis for the first fiber placement machines.
The mechanism for splitting was put on the head of the machine for placing fibers. Its job was to separate a 3-inch-wide tape into 24 strands. These strings are called “tows.”
Before, it wasn’t easy to lay up wider tapes on parts with a lot of curves. But it was easy to lay down wider tows on any surface with this machine.
1980 was the year that Hercules made its first Automated Fiber Placement machine, which was made possible by more work on the slitting mechanism. The machine had the cut-restart feature of ATL and the differential payout feature of filament winding.
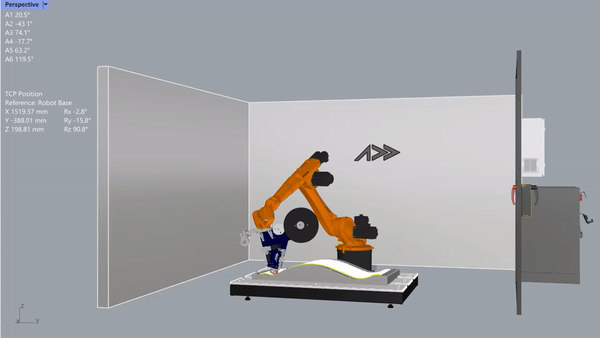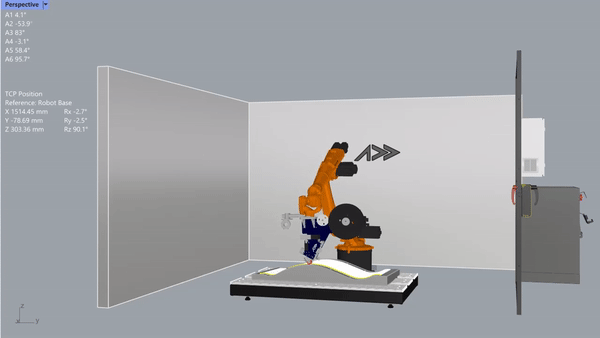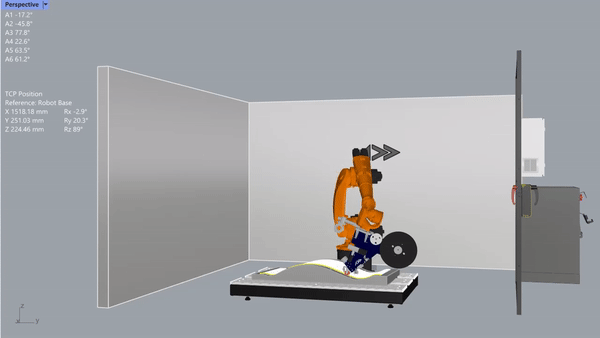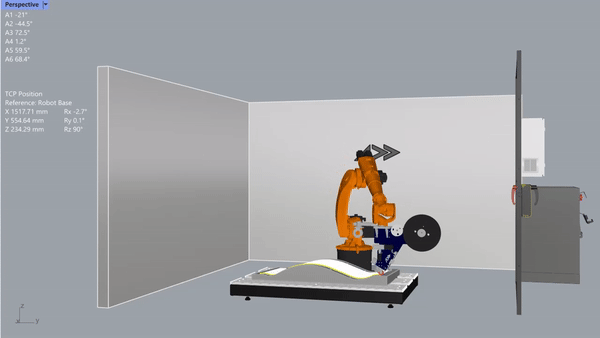
After a few years, he made more and put them up for sale. Northrop and Boeing, which work in the space industry, liked them.
Later, makers like Bullock changed how the AFP machines guided the material and how the rollers worked. Also, they used ATL’s method for heating materials. It could also change the temperature, pressure, and tow of the layup.
speed, and tension.
Benson and Grant’s report from 1993 says that the Automated Fiber Placement machine got better. The previous invention had problems with the creel, so they changed the way the creel worked in the new one.
The machine could also unwind smoothly, and the material it made could last longer.
Later, in the 1990s, the AFP process became more productive. In return, the machine got better and easier to use. Manufacturers took advantage of the improvement of the machine and began making
composites of thermoplastics. These materials were used to make structures that were perfect for space travel.
But the composite structures made with thermoplastic layups were bigger than what was needed for the plastic to harden. Because of this, more research was done.
In the 2000s, Boing and Electroimpact started looking into how to improve the reliability and productivity of the fiber placement machine.
They could do a number of manual checks and fix the AFP layups. According to the report from both companies, it took a lot of time to inspect, make changes to the layout, and finish the whole process.
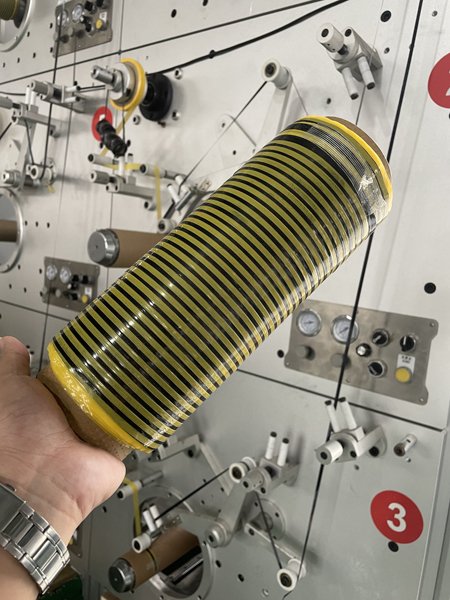

That’s when Engelbart and others came up with an automated system that could find problems in different places. By using data about where something is, the machine could use electronics to find a problem anywhere and point it out.
Engelbart and his colleagues also made a fast system with two heads that can be switched out. Also, it cut down on the length of the towpath of that better AFT machine.
Later on, Flynn invented a more efficient fiber placement machine with multiple cells and modular heads. The machine featured;
- Automatic heads that could rotate up to 360 degrees
- Production of different tow widths
- Offline maintenance
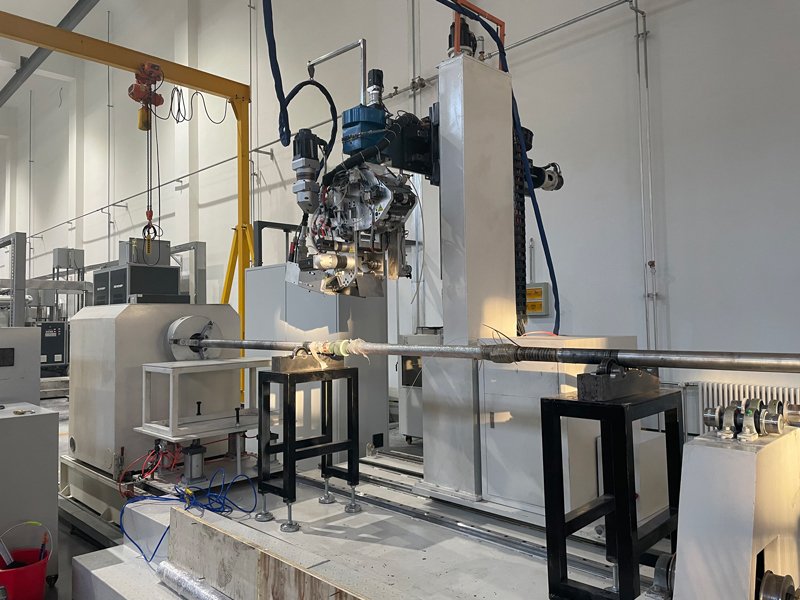
In 2013, highly accurate robots emerged, recording a breakthrough of better fiber placement machines. Recent AFP machines produce in-situ layups with minimal defects. As a result, they made high-quality AFP manufactured structures.
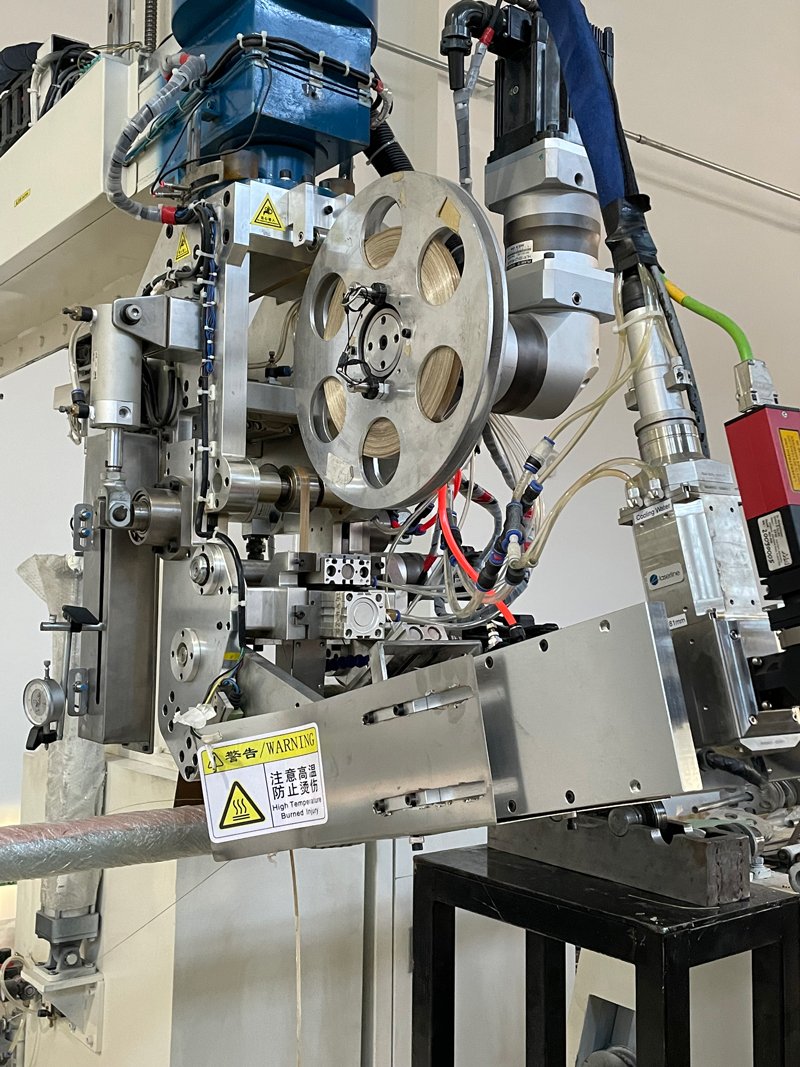
At Jota Machinery, we use the latest technology to make our AFP machines. We also make them in different types but consists of similar hardware.
For a better understanding, below are their types and central parts.
Jota Machinery AFP Machine Types
They include;
- The horizontal gantry
We make them with a robot containing 6 degrees of freedom (DOF). Three are rotational with an extra external rotational axis used on the tool. The other three are Cartesian.
They are used on any part with a height or require rotation.
- Vertical gantry
Its operation is similar to the horizon gantry’s, but the head does the layup from the tool’s top. Also, it does not rotate the mandrel.
A vertical gantry machine work on large plate-like structures. The motion involved is less complex.
- Robotic arm
The robotic arm has six degrees of freedom (DOF), just like the horizontal gantry machine. It also has a straight line. If you add a rotator, the DOF will go up to 8. With this machine, you can lay up tools set horizontally, vertically, or in a circle.
It is the most versatile of the three types because it can move in more ways and make great complex shapes.
The machine used to place fibers depends on the size and shape of the part being made.
Now that you know the different kinds of Automated Fiber Placement machines, let’s look at their different parts.
Components of AFP Machines from Jota Machinery
Our AFP machines consist of various parts as described below;
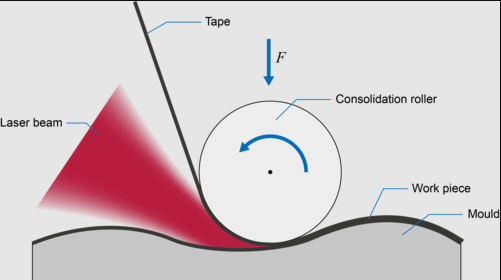
- Compaction Rollers
Their function entails the following;
- Place tows
- Help develop the needed tack levels
- Minimize voids between tows
The rollers begin by applying a substrate and pressure to the tows after the heat is applied. The aim is to achieve proper adhesion, which prevents manufacturing defects.
Compaction rollers come either as solid or segmented.
- Solid Compaction Rollers
You can find these compaction rollers in AFP heads that are made to build small structures. Rollers can be solid or have holes in them. Before you use these rollers, you need to think about how hard they are.
A durometer scale is used to measure how hard something is. If the reading level is high, it means the material is hard. The roller will put more force on the tow, but only in a small area, the stiffer it is. Softer rollers spread less pressure over a large area, which is why users prefer them.
- Segmented Compaction Rollers
We make them for industrial manufacturing AFP machines. The segmented rollers entail many small rollers that move independently on one shaft. Each small roller contains a metal material inside and a flexible cover on the outside.
Segmented compaction rollers enhance optimal force control during the entire procedure. The roller’s uniform pressure distribution ensures the proper tow placement.
- Thermoplastic Compaction
The thermoplastic materials worked on by the AFP machines require an extreme heating and cooling system.
The thermoplastic compaction consists of a highly effective heating and cooling system. It works as follows;
- The first hotline area starts the contact and healing process.
- Then the second hotline takes over to maintain the temperature to ensure the polymer chains heals wholly and appropriately.
- The last line is the cold compactor. It cools the material and presses it to prevent voids.
Because these rollers encounter high temperatures, the material we use in making them is steel.
- The Heat Supply Part
The part that supplies heat in an ATP machine is a heater. It’s usually located on the ATP machine’s head and enables the incoming tows to stick firmly to each other.
We install various types of heaters in our AFP machines Heaters in AFP machines. They include;
- Hot gas torches (HGT); use a hot gas like nitrogen to heat the material. It’s cheap to use but challenging to control the temperature.
- Infrared (IR) heaters; We install them in our AFP machines that manufacture thermoset materials. Heat transfer happens through radiation. Unfortunately, the heat disperses widely, causing non-uniformity in heat spreading. Also, they produce insufficient heat for thermoplastic materials.
- Lasers; Compared to the other kinds, the laser heaters heat better. They are also easy on the wallet, which makes them popular on the market. We put in the newer ones because they don’t hurt the material and give off a lot of energy. The heat is also more focused, works faster, and gives the surface a better finish.
Unlike other heating types, you will need to take safety precautions for yourself and the AFP cell when using lasers to prevent damage. Also, working on a glass fiber material using a laser would be in vain because it wouldn’t absorb its energy.
- Pulsed light heaters; It’s a recent heat source invention. We use it in some of our AFT machines. The system delivers heat using voltage pulse duration, and frequency parameters.
- Modular Heads
You will find them in modern Automated Fiber Placement machines. Their rate and quality are high, explaining why manufacturers utilize them to produce commercial aircraft structures. The modular heads also make many tow widths, while their maintenance happens offline.
While in operation, you can also change the head rapidly and take a short towpath.
- The Tool
It’s another name for the surface to lay the material. The tool comes in the shape the final structure will possess. Structural components made on tools include those for;
- Marine vehicles
- Aircraft
- Space vehicles
The tool’s geometry may vary based on the structure to get produced. To better understand the AFP process, you need to know what tool geometries entail.
About Tool Geometries
It’s the shape of the tool that determines the shape of the final structure. The forms can either be;
- Flat; it’s not popular in ATP machines because the hand layups or ATL manufacturing techniques can handle it. But some complex tooling has them.
- Singly Curved; these kinds of tools produce sections of fuselages or wings. They are usually open or closed contour surfaces. You will need to mount a closed contour surface, like a cylinder, on the rotating mandrel.
- Doubly or Complex Curved; makes robust structures like blended wing bodies and wind tunnel blades.
You may wonder why tool geometries are crucial. Here are the reasons;
Why Do Tool Geometries Matter in AFP Manufacturing Processes
If not of the best quality, the tool may bring forth the following problems;
- Impair the layup quality
- Gaps presence
- Defects in bridging and overlaps
- Decreased pressure uniformity
- Wrinkles on the final structure
Also, severe curvatures emerge if the AFP machine collides with a curved tool. In return, the machine may not reach such areas, creating a wrongly formed structure.
With the above knowledge on how the Automated Fiber Placement technology came about and the machines used, you may wonder how the process happens. No need to fret; check out the following;
The Automated Fiber Placement Process
It entails the following several phases;
Phase 1: Planning Stage
It’s the first step of the AFP process. You start by planning how to complete the layup. You will require effective strategies directing you on;
- Where to start
- Reference curves
- The surface’s coverage area
Phase 2: Strategy Implementation
It’s the second stage of the AFP technique. You implement the laid-out strategies in the planning phase as planned. Start by creating an ideal reference or guide curve before covering the tool with toolpaths.
Then create course centerlines on the tool’s surface using the planned strategies. You can make the course centerlines using shifted, offset, or independent curve methods.
Phase 3: Optimize the Toolpath
After creating centerlines across the tool, optimize the fiber placement paths on the tool’s surface. It will help reduce path errors during the process.
Phase 4: Start the AFP Manufacturing Process
With the above phases set, you can now start your AFP machine. The layup quality would be excellent if you did the previous stages right and the speed was okay. Other parameters that determine the quality of the final composite structure includes;
- Pressure
- Tow tension
- Temperature
Watch the following video to see how Automated Fiber Placement machines work.
Though Jota Machinery uses the latest technology to make top-notch AFP machines, we shall not stop improving and updating. So, how will the AFP’s future be? Here is the answer;
The Future of Automated Fiber Placement
We hope that our AFP machines will help make the world a better place by making AFP better in the future. It means making it easier for people to use new technology and making things easier to do.
Designing composite materials will also get better, and there will be a big drop in problems with hardware, process planning, inspection, and tools.
Also, the inspection area would make it easy and quick to spot problems, leading to great accuracy.
Conclusion
As shown above, Automated Fiber Placement technology is an important part of making things. Even though they help make structures out of composite materials, they also make those structures strong.
Fiber-placing machines have also changed over time, making it possible for many industries to build high-quality structures on a large scale.
Get in touch with us today if you have any questions or want to order the best AFP machinery for your factory.
What’s impressive is that the AFP future looks promising!
We Jota could also supply the following related machines if you are also interested in any type, please feel free to send us an inquiry:
- Hot Melt Thermoplastic CFRP CFRTP Prepreg Manufacturing Machine
- Fully Automatic Toilet Paper Maker
- Automatic Facial Tissue Making Machine
- Fully Automatic Thermal Paper Roll Slitting Packing Machine
- Plastic Film, Fabric, Aluminum Foil Slitting Rewinding Machine
- Paper Sheeter
- Paper Tube Making Machine
- CFRP CFRTP FRP Prepreg Slitter
- Paper Drinking Straws Machine
- Label Die Cutting Machine
- Flexo Printing Machine
- Cardboard Tube Cutting Machine